A software-defined network (SDN) is an approach to network management that enables dynamic and programmatically network configuration.
This is a contrast with traditional networks, where the network is defined by using hardware components.
An SDN looks like a single logical network.
SDN would be the counterpart on network management to other approaches, like cloud computing to computer resource management or infrastructure as code (IaC) to configuration management.
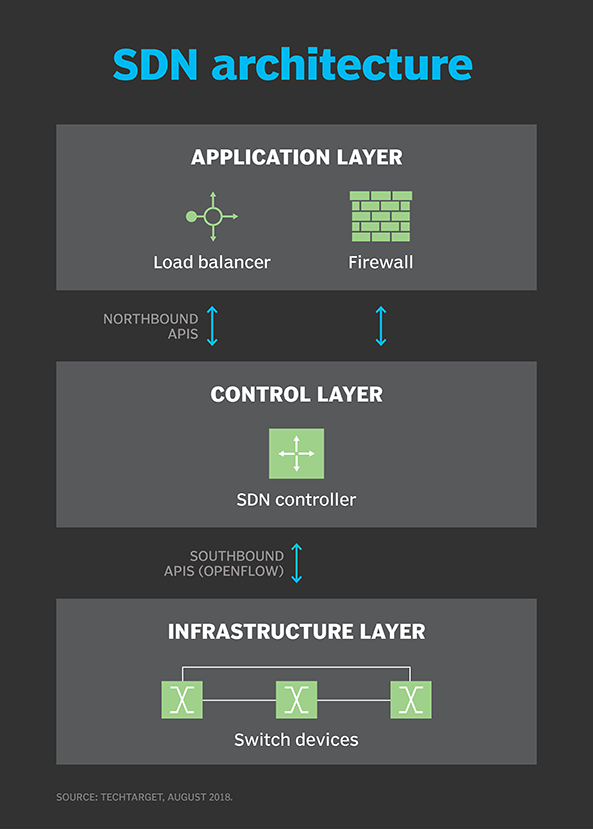
SDN Architecture
SDN Elements
SDN elements:
- SDN controller
- Southbound interface (SBI)
- Northbound interface (NBI)
An SDN controller is the core element in SDN architecture that manages flow control for network management and application performance centrally across physical and virtual network environents. You can read this external link about SDN controller.
A southbound interface (SBI) or southbound API relays information between the controller and the individual network devices (such as switches, access points, routers, and firewalls).
A northbound interface (NBI) handles the traffic between the SDN controllers and the SDN applications and policy engines.
SD-WAN
Software-defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) is commonly used to manage multiple ISPs and other connectivity options to ensure speed, reliability and bandwith design goals.
- Combines active data collection via monitoring
- Response via self-learning and machine intelligence techniques
- Apply predefined rules to take action to make the network perform as desired.
You might also be interested in…
External References
- Wikipedia community; “Software-defined network“; Wikipedia
- ; “SDN controller (software-defined networking controller)“; TechTarget